Unsettling Evidence on COVID-19 Vaccines: A Closer Look at Mortality Risks
Disclaimer: This post is for informational purposes only and not medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare professional for medical concerns.
The rapid development and deployment of COVID-19 injectables were heralded as a triumph of modern science, yet emerging data since the global rollout raises critical questions about their actual safety and efficacy. Two pivotal studies, one co-authored by myself, Daniel Santiago, analyzing UK data, and another examining Florida residents, reveal troubling associations between COVID-19 vaccinations and significant increases all-cause mortality. This article synthesizes the findings from both studies, urging a reevaluation of the public health narrative surrounding these genetic interventions.
UK Data: A Near-Perfect Correlation with Death
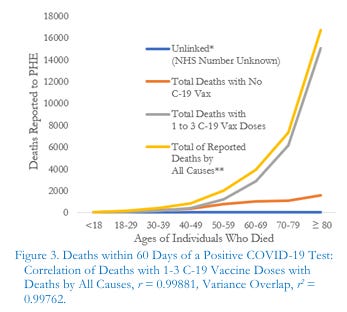
In our peer-reviewed study, published in the International Journal of Vaccine Theory, Practice, and Research (Oller & Santiago 2022), we analyzed 28 weeks of Public Health England (PHE) data from 2021 to 2022. The dataset tracked deaths within 60 days of a positive COVID-19 test, segmented by age and vaccination status.
Our findings were startling: a near-perfect correlation (r = 0.99881) emerged between deaths among those who received one to three doses of Pfizer, Moderna, or AstraZeneca “vaccines” and total deaths from all causes. Among the 16,724 deaths recorded, 15,055 (90%) occurred among vaccinated individuals, compared to just 1,612 (9.6%) among the unvaccinated.
Fig 1- Oller & Santiago (2022)
This correlation challenges the assumption formed, not doubt, by repeated claims from authority figures that vaccination reduces mortality risk.
The data suggests, instead, that the injectables, heavily marketed as vaccines, may not only fail to protect against COVID-19-related deaths but could represent contributing factors to mortality. The study highlights the complexity of the vaccines’ mRNA technology, which replaces uridine with N1-methylpseudouridine to enhance spike protein production. This modification, intended to evade immune detection, may disrupt the body’s maintenance-repair-defense (MRD) systems, potentially leading to unintended health consequences, such as autoimmune reactions or liver cell DNA alterations (Aldén et al. 2022).
The UK Health Security Agency’s rationale, that high vaccination coverage explains the disproportionate deaths among the vaccinated, falls short. With 74–95% of adults vaccinated, the sheer scale of deaths (9.3 vaccinated deaths for every unvaccinated death) suggests a causal link that cannot be dismissed as a mere statistical artifact. The cessation of detailed mortality reporting after week 12 of 2022 further fuels concerns about transparency.
Florida Study: Differential Risks Between mRNA Vaccines
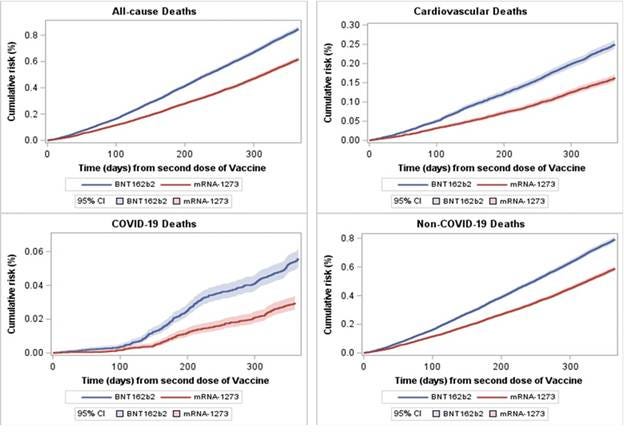
A complementary study by Levi et al. (2025), published as a preprint on medRxiv, compared 12-month mortality outcomes among 1.47 million matched Florida residents who received two doses of either Pfizer’s BNT162b2 or Moderna’s mRNA-1273 vaccine. The results revealed significantly higher risks for BNT162b2 recipients across multiple endpoints:
All-cause mortality: 847.2 (Pfizer) vs. 617.9 (Moderna) deaths per 100,000 (OR 1.384, 95% CI [1.331, 1.439]).
Cardiovascular mortality: 248.7 (Pfizer) vs. 162.4 (Moderna) deaths per 100,000 (OR 1.540, 95% CI [1.431, 1.657]).
COVID-19 mortality: 55.5 (Pfizer) vs. 29.5 (Moderna) deaths per 100,000 (OR 1.882, 95% CI [1.596, 2.220]).
Non-COVID-19 mortality: 791.6 (Pfizer) vs. 588.4 (Moderna) deaths per 100,000 (OR 1.356, 95% CI [1.303, 1.412]).
Despite meticulous matching for age, sex, race, ethnicity, vaccination site, and census tract, these differences remained, effectively reducing potential confounding factors such as healthy vaccinee bias. The study's negative control outcomes, suicide and homicide deaths, showed no significant variation, further supporting the reliability of the findings. Notably, these results are unexpected, considering that Moderna's mRNA-1273 vaccine delivers roughly three times the mRNA content (100 µg) compared to Pfizer's BNT162b2 vaccine (30 µg).
Remarkably, the increased mortality risk was most pronounced in adults over 60, with cardiovascular and COVID-19 mortality curves diverging significantly after 30–200 days post-vaccination.
Fig 2- Levi et al (2025)
The authors speculate that differences in mRNA dosage, lipid nanoparticle composition, or manufacturing processes between BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 may explain these outcomes. This divergence aligns with prior studies undertaken by Veterans Affairs, which also found higher cardiovascular risks with BNT162b2 (Dickerman et al. 2022).
Converging Evidence, Diverging Narratives
Both studies underscore a critical point: the assumption that COVID-19 vaccines are uniformly “safe and effective” is not supported by empirical data. The UK study suggests that the injectables may be driving mortality, potentially through mechanisms such as immune suppression or cross-reactivity (Seneff et al. 2022, Vojdani et al. 2021). The Florida study highlights differential risks between mRNA vaccines, raising questions about their non-specific effects on health.
The public narrative, heavily influenced by government and pharmaceutical interests, has downplayed these risks, often framing vaccines as the sole solution to the pandemic. Yet, the 40% rise in all-cause mortality in the US in 2021 (Berdine 2022) and the increasing proportion of deaths among vaccinated individuals (Mitropoulos 2022) demand careful scrutiny. The reliance on booster shots to address waning immunity ignores the possibility that the injectable product themselves may exacerbate vulnerability to disease.
A Call for Transparency and Action
These findings call for rigorous, independent assessment of these new genetic interventions. The complexity of mRNA technology, along with its potential to disrupt essential biological systems, warrants further in-depth studies. Public health authorities must:
Resume transparent reporting of mortality data by vaccination status, as the UK’s cessation of such reports hinders accountability.
Conduct randomized trials comparing mRNA vaccines against each other and placebos, focusing on all-cause mortality and long-term health outcomes.
Investigate biological mechanisms behind the observed mortality risks, including the role of lipid nanoparticles and spike protein production.
As a pharmacist, I’ve witnessed firsthand over many years the trust that patients place in medical interventions. That unquestioning trust is now fast eroding as evidence of harm continues to mount. We owe it to the public to confront these data head-on, prioritizing empirical science over political dogma. The stakes, human lives, are too high for anything less.
As Gayle Delong noted in the last paper she finished just a few days before her death, correlation is not a proof of causation all by itself, but causation is a proof of correlation, and a perfect positive correlation where a negative should be expected by standard vaccine theory suggests a powerful causal relation. Vaccinating people one or more times to prevent death from COVID-19 should not increase their likelihood of their dying from COVID-19.
Disclaimer: This post is for informational purposes only and not medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare professional for medical concerns.
References
Aldén, M., Olofsson Falla, F., Yang, D., Barghouth, M., Luan, C., Rasmussen, M., & De Marinis, Y. (2022). Intracellular reverse transcription of Pfizer BioNTech COVID-19 mRNA vaccine BNT162b2 in vitro in human liver cell line. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 44(3), 1115–1126. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44030073
Berdine, G. (2022, January 30). All cause mortality in the United States during 2021. American Institute for Economic Research. https://www.aier.org/article/all-cause-mortality-in-the-united-states-during-2021/
Dickerman, B. A., Madenci, A. L., Gerlovin, H., et al. (2022). Comparative safety of BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 vaccines in a nationwide cohort of US veterans. JAMA Internal Medicine, 182(7), 739–746. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2022.2109
Levi, R., Mansuri, F., Jordan, M. M., & Ladapo, J. A. (2025). Twelve-month all-cause mortality after initial COVID-19 vaccination with Pfizer-BioNTech or mRNA-1273 among adults living in Florida. medRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2025.04.25.25326460
Mitropoulos, A. (2022, May 10). Breakthrough deaths comprise increasing proportion of those who died from COVID-19. ABC News. https://abcnews.go.com/Health/breakthrough-deaths-comprise-increasing-proportion-died-covid-19/story?id=84627182
Oller, J. W., Jr., & Santiago, D. (2022). All cause mortality and COVID-19 injections: Evidence from 28 weeks of Public Health England “COVID-19 vaccine surveillance reports”. International Journal of Vaccine Theory, Practice, and Research, 2(2), 301–318. https://doi.org/10.56098/ijvtpr.v2i2.42
Seneff, S., Nigh, G., Kyriakopoulos, A. M., & McCullough, P. A. (2022). Innate immune suppression by SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccinations: The role of G-quadruplexes, exosomes, and MicroRNAs. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 164, 113008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2022.113008
Vojdani, A., Vojdani, E., & Kharrazian, D. (2021). Reaction of human monoclonal antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 proteins with tissue antigens: Implications for autoimmune diseases. Frontiers in Immunology, 11, 617089. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.617089